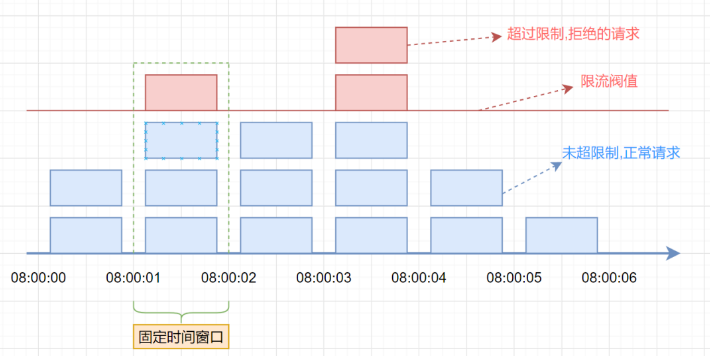
固定窗口限流算法
首维护一个计数器,将单位时间段当做一个窗口,计数器记录这个窗口接收请求的次数。
当次数少于限流阀值,就允许访问,并且计数器+1
当次数大于限流阀值,就拒绝访问。
当前的时间窗口过去之后,计数器清零。
假设单位时间是1秒,限流阀值为3。在单位时间1秒内,每来一个请求,计数器就加1,如果计数器累加的次数超过限流阀值3,后续的请求全部拒绝。等到1s结束后,计数器清0,重新开始计数。如下图:
伪代码如下:
/**
* 固定窗口时间算法
* @return
*/
boolean fixedWindowsTryAcquire() {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取系统当前时间
if (currentTime - lastRequestTime > windowUnit) { //检查是否在时间窗口内
counter = 0; // 计数器清0
lastRequestTime = currentTime; //开启新的时间窗口
}
if (counter < threshold) { // 小于阀值
counter++; //计数器加1
return true;
}
return false;
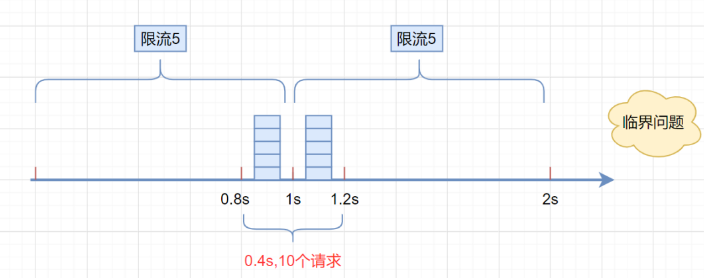
}但是,这种算法有一个很明显的临界问题:假设限流阀值为5个请求,单位时间窗口是1s,如果我们在单位时间内的前0.8-1s和1-1.2s,分别并发5个请求。虽然都没有超过阀值,但是如果算0.8-1.2s,则并发数高达10,已经超过单位时间1s不超过5阀值的定义啦。
滑动窗口限流算法
滑动窗口限流解决固定窗口临界值的问题。它将单位时间周期分为n个小周期,分别记录每个小周期内接口的访问次数,并且根据时间滑动删除过期的小周期。
一张图解释滑动窗口算法,如下:
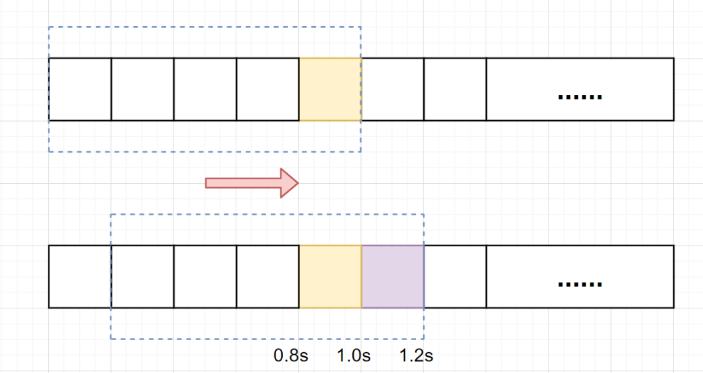
假设单位时间还是1s,滑动窗口算法把它划分为5个小周期,也就是滑动窗口(单位时间)被划分为5个小格子。每格表示0.2s。每过0.2s,时间窗口就会往右滑动一格。然后呢,每个小周期,都有自己独立的计数器,如果请求是0.83s到达的,0.8~1.0s对应的计数器就会加1。
我们来看下滑动窗口是如何解决临界问题的?
假设我们1s内的限流阀值还是5个请求,0.8~1.0s内(比如0.9s的时候)来了5个请求,落在黄色格子里。时间过了1.0s这个点之后,又来5个请求,落在紫色格子里。如果是固定窗口算法,是不会被限流的,但是滑动窗口的话,每过一个小周期,它会右移一个小格。过了1.0s这个点后,会右移一小格,当前的单位时间段是0.2~1.2s,这个区域的请求已经超过限定的5了,已触发限流啦,实际上,紫色格子的请求都被拒绝啦。
TIPS: 当滑动窗口的格子周期划分的越多,那么滑动窗口的滚动就越平滑,限流的统计就会越。
滑动窗口算法伪代码实现如下:
/**
* 单位时间划分的小周期(单位时间是1分钟,10s一个小格子窗口,一共6个格子)
*/
private int SUB_CYCLE = 10;
/**
* 每分钟限流请求数
*/
private int thresholdPerMin = 100;
/**
* 计数器, k-为当前窗口的开始时间值秒,value为当前窗口的计数
*/
private final TreeMap<Long, Integer> counters = new TreeMap<>();
/**
* 滑动窗口时间算法实现
*/
boolean slidingWindowsTryAcquire() {
long currentWindowTime = LocalDateTime.now().toEpochSecond(ZoneOffset.UTC) / SUB_CYCLE * SUB_CYCLE; //获取当前时间在哪个小周期窗口
int currentWindowNum = countCurrentWindow(currentWindowTime); //当前窗口总请求数
//超过阀值限流
if (currentWindowNum >= thresholdPerMin) {
return false;
}
//计数器+1
counters.get(currentWindowTime)++;
return true;
}
/**
* 统计当前窗口的请求数
*/
private int countCurrentWindow(long currentWindowTime) {
//计算窗口开始位置
long startTime = currentWindowTime - SUB_CYCLE* (60s/SUB_CYCLE-1);
int count = ;
//遍历存储的计数器
Iterator<Map.Entry<Long, Integer>> iterator = counters.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Long, Integer> entry = iterator.next();
// 删除过期的子窗口计数器
if (entry.getKey() < startTime) {
iterator.remove();
} else {
//累加当前窗口的所有计数器之和
count =count + entry.getValue();
}
}
return count;
}滑动窗口算法虽然解决了固定窗口的临界问题,但是还是有一些问题:因为滑动窗口算法,需要将请求记录起来,然后下次请求来的时候,要把过期的请求清空,然后再计算数量,这个比较耗费时间,thinkphp6的Throttle中间件就是这个算法。
class Throttle
{
/**
* 缓存对象
* @var Cache
*/
protected $cache;
/**
* 配置参数
* @var array
*/
protected $config = [
// 缓存键前缀,防止键值与其他应用冲突
'prefix' => 'throttle_',
// 节流规则 true为自动规则
'key' => true,
// 节流频率 null 表示不限制 eg: 10/m 20/h 300/d
'visit_rate' => null,
// 访问受限时返回的http状态码
'visit_fail_code' => 429,
// 访问受限时访问的文本信息
'visit_fail_text' => 'Too Many Requests',
];
protected $wait_seconds = 0;
protected $duration = [
's' => 1,
'm' => 60,
'h' => 3600,
'd' => 86400,
];
protected $need_save = false;
protected $history = [];
protected $key = '';
protected $now = 0;
protected $num_requests = 0;
protected $expire = 0;
public function __construct(Cache $cache, Config $config)
{
$this->cache = $cache;
$this->config = array_merge($this->config, $config->get('throttle', []));
}
/**
* 生成缓存的 key
* @param Request $request
* @return null|string
*/
protected function getCacheKey($request)
{
$key = $this->config['key'];
if ($key instanceof \Closure) {
$key = call_user_func($key, $this, $request);
}
if (null === $key || false === $key || null === $this->config['visit_rate']) {
// 关闭当前限制
return;
}
if (true === $key) {
$key = $request->ip();
} elseif (false !== strpos($key, '__')) {
$key = str_replace(['__CONTROLLER__', '__ACTION__', '__IP__'], [$request->controller(), $request->action(), $request->ip()], $key);
}
return md5($this->config['prefix'] . $key);
}
/**
* 解析频率配置项
* @param $rate
* @return array
*/
protected function parseRate($rate)
{
list($num, $period) = explode("/", $rate);
$num_requests = intval($num);
$duration = $this->duration[$period] ?? intval($period);
return [$num_requests, $duration];
}
/**
* 计算距离下次合法请求还有多少秒
* @param $history
* @param $now
* @param $duration
* @return void
*/
protected function wait($history, $now, $duration)
{
$wait_seconds = $history ? $duration - ($now - $history[0]) : $duration;
if ($wait_seconds < 0) {
$wait_seconds = 0;
}
$this->wait_seconds = $wait_seconds;
}
/**
* 请求是否允许
* @param $request
* @return bool
*/
protected function allowRequest($request)
{
$key = $this->getCacheKey($request);
if (null === $key) {
return true;
}
list($num_requests, $duration) = $this->parseRate($this->config['visit_rate']);
$history = $this->cache->get($key, []);
$now = time();
// 移除过期的请求的记录
$history = array_values(array_filter($history, function ($val) use ($now, $duration) {
return $val >= $now - $duration;
}));
if (count($history) < $num_requests) {
// 允许访问
$this->need_save = true;
$this->key = $key;
$this->now = $now;
$this->history = $history;
$this->expire = $duration;
$this->num_requests = $num_requests;
return true;
}
$this->wait($history, $now, $duration);
return false;
}
/**
* 处理限制访问
* @param Request $request
* @param Closure $next
* @return Response
*/
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
$allow = $this->allowRequest($request);
if (!$allow) {
// 访问受限
$code = $this->config['visit_fail_code'];
$content = str_replace('__WAIT__', $this->wait_seconds, $this->config['visit_fail_text']);
$response = Response::create($content)->code($code);
$response->header(['Retry-After' => $this->wait_seconds]);
return $response;
}
$response = $next($request);
if ($this->need_save && 200 == $response->getCode()) {
$this->history[] = $this->now;
$this->cache->set($this->key, $this->history, $this->expire);
// 将速率限制 headers 添加到响应中
$remaining = $this->num_requests - count($this->history);
$response->header([
'X-Rate-Limit-Limit' => $this->num_requests,
'X-Rate-Limit-Remaining' => $remaining < 0 ? 0: $remaining,
'X-Rate-Limit-Reset' => $this->now + $this->expire,
]);
}
return $response;
}
public function setRate($rate)
{
$this->config['visit_rate'] = $rate;
}
}令牌桶算法
面对突发流量的时候,我们可以使用令牌桶算法限流。
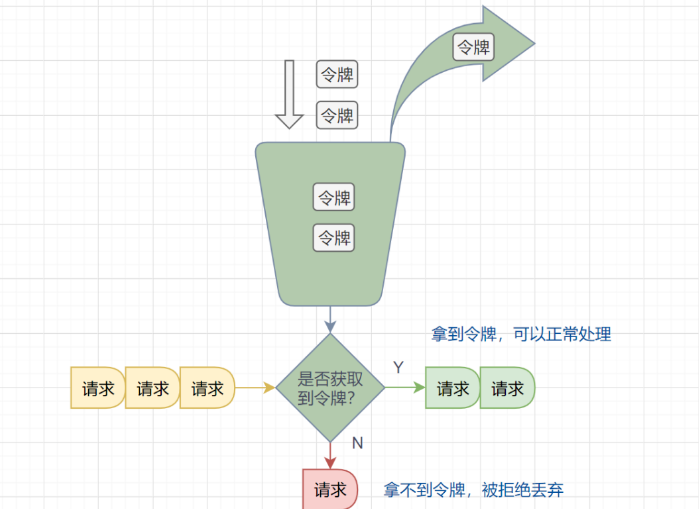
令牌桶算法原理:
- 有一个令牌管理员,根据限流大小,定速往令牌桶里放令牌
- 如果令牌数量满了,超过令牌桶容量的限制,那就丢弃。
- 系统在接受到一个用户请求时,都会先去令牌桶要一个令牌。如果拿到令牌,那么就处理这个请求的业务逻辑;
- 如果拿不到令牌,就直接拒绝这个请求
漏桶算法伪代码实现如下:
/**
* 每秒处理数(放入令牌数量)
*/
private long putTokenRate;
/**
* 后刷新时间
*/
private long refreshTime;
/**
* 令牌桶容量
*/
private long capacity;
/**
* 当前桶内令牌数
*/
private long currentToken = 0L;
/**
* 漏桶算法
* @return
*/
boolean tokenBucketTryAcquire() {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取系统当前时间
long generateToken = (currentTime - refreshTime) / 1000 * putTokenRate; //生成的令牌 =(当前时间-上次刷新时间)* 放入令牌的速率
currentToken = Math.min(capacity, generateToken + currentToken); // 当前令牌数量 = 之前的桶内令牌数量+放入的令牌数量
refreshTime = currentTime; // 刷新时间
//桶里面还有令牌,请求正常处理
if (currentToken > 0) {
currentToken--; //令牌数量-1
return true;
}
return false;
}参考
https://z.itpub.net/article/detail/B049B6F216829EDD0827E97BC1AA9100
